Movies and scientific technology have a tremendous influence on each other. Movies about robots inspire scientists, and advances in science and technology provide ideas and information to movie makers. With the convergence of artificial intelligence and the Fourth Industrial Revolution, robotic technology is not only inducing human-robot interaction but is also leading us into a future that goes beyond our wildest imagination.
Robots in cinema – The crossroads between utopia and dystopia
When someone asks for help from Andrew—the robot in the movie Bicentennial Man (2000)—he answers, “One is glad to be of service.” Even though his abilities surpass that of any human, he dedicates himself to serving humankind until his last moments.
On the other hand, Ex Machina (2015) deals with the Turing test process for an intelligent humanoid robot endowed with dangerous charm. The robot feels human emotions and experiences confusion, ultimately killing the man who developed her, and hides by blending into society.
The Terminator series depicts the desperate and gloomy world of a dystopia dominated by robots. However, in George Lucas’s movie series Star Wars, robots with their own distinct personalities play active roles, such as the friendly and intelligent R2-D2, not to mention the talkative and pompous C-3PO.
The novel I, Robot, by science fiction writer Isaac Asimov, was published in 1950 and made into a movie in 2004. In the novel, the author expands without limit the imagined fear of robots collectively rebelling against humans, raising questions about human existence and technology.
A highly diverse evolution of trends in robotic technology
Robotic technology has an “invisible engine” that converges the technologies and knowledge of the Fourth Industrial Revolution such as AI, Internet of Things, wireless internet, and 3D printing. From humanoid and collaborative robots, companion robots, and combat robots to delivery and surgical robots, this convergence continues to realize unprecedented innovative achievements.
Robots, as machines that work, think, and make judgments on their own, can look like humans, but they can also take the shape of a simple speaker like Amazon Echo. Atlas—the biped humanoid robot developed by Boston Dynamics, a company acquired by the Hyundai Motor Group in 2020—demonstrates jumping movements that are as fluid and authentic as those of a real living being.
Not only that, but the Hyundai Motor Group has developed the wearable robot VEX, which is worn and used by workers who must keep their arms raised in order to work in places such as car assembly factories. VEX is a wearable robot that mimics human shoulder joints and increases productivity while reducing fatigue. It has led to the development of agricultural robots in 2021.
Intelligent robots perform their functions through AI command and operation. In addition to the movement of joints in their wrists, ankles, and fingers and sensory functions such as sight, touch, and hearing, such robots also have cognitive functions such as learning, association, memory, and reasoning.
Created in Italy through AI, iCub is a 1-meter tall open-source humanoid. The 2022 version of this robot, which is now 13 years old, can express emotions, solve complex 3D mazes, shoot arrows, and catch small objects, and is now at the level of playing with children in human form. There is also Pepper, a humanoid robot developed by SoftBank Robotics in France, that recognizes emotions. Pepper is a companion robot with a cute appearance resembling that of a child, and that can talk and move while recognizing human emotions. Companion robots can affect communications among family members and take care of the elderly and the physically challenged in connection with medical services. These robots are able to evolve by studying the behaviors of the humans around them.
Starship Technology, a British robot development venture, has completed more than 2.5 million deliveries through robots as of February 2022 since its establishment in 2014. The company is presently testing Starship Robots—autonomous delivery robots—in more than 100 cities in 20 countries. Although their robots each look like a small box, they can carry up to 45 kg and travel at a speed of 6.4 km per hour, resulting in post offices and pizza companies adopting them for business.
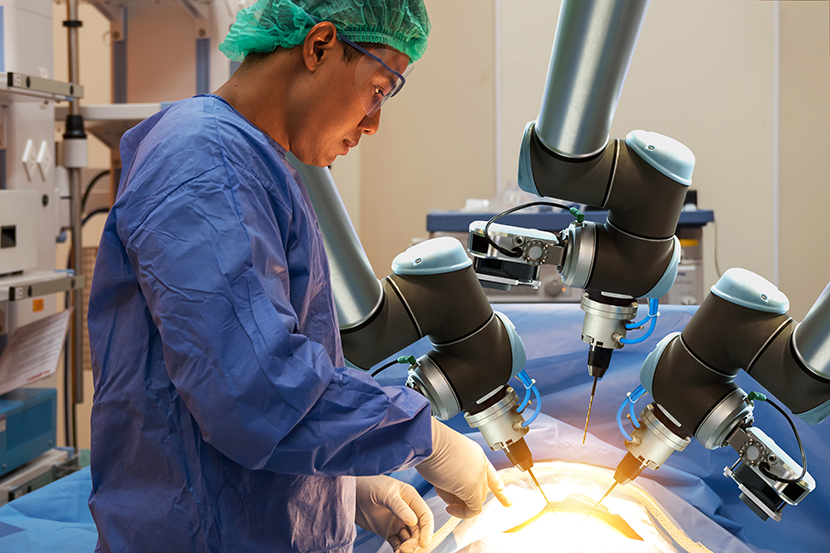
There are also cases of surgery and treatments performed using robots. The Da Vinci robotic-assisted surgery system used in hospitals can conduct a variety of functions, including securing high-definition 3D images and a field of view magnified up to 10 times. With the Da Vinci System, doctors can have small instruments inside the patient’s body imitate their hand movements to perform surgeries.
Military robots are deployed for reconnaissance, observation, photography, and targeted strikes. In 2020, the drone robot STM Kargu carried out an attack in Libya with explosives mounted on it, through AI and without direct human control. The use of military robots in battle first took place during the wars in Afghanistan in 2001 and in Iraq in 2004.
Robots, the greatest convergence technology invented by humankind
The imagination appearing in sci-fi robot movies is being implemented in earnest as real technology that expands, assists, collaborates, or replaces human labor. They can assemble automobiles and home appliances on the production line on behalf of humans, and can also develop and create products in collaboration with experts. They are replacing teachers by ubiquitously providing help for students to learn new languages and study science based on AI algorithms, and they are also working in dangerous disaster sites or are exploring outer space in places such as Mars on behalf of humans. They are changing our world.
In his robot stories, Isaac Asimov suggested three essential laws for robots: they must not harm humans, they must obey human commands, and they must protect themselves. These principles reflect not only hope for the future of robotics but also raise the fear of the possibility of intelligent robots developing their own feelings and emotions to eventually rebel against humans. In many aspects, robots are the greatest convergence technology invented by humanity. With infinite development potential at a level that is difficult to predict, measure, or even imagine, they are a phenomenon that evokes imagination, hope, and fear all at the same time.
With contact-free communication becoming the norm due to the COVID-19 pandemic, many more companies are showing interest in robot technology. Today, we have reached an era where the philosophy and perspective that all technologies in the world exist for the development and happiness of the community are becoming more important. Deep and thorough contemplation is required for robot technology, which is closely affecting various industries and the daily life of people.
It is therefore necessary to continuously prepare measures through free and active social discussions and research in order for robotic technology to play a positive role in our future society.
Writer Professor Kong Byoung-hun, Department of Media and Advertising, Hyupsung University
2022.04.14